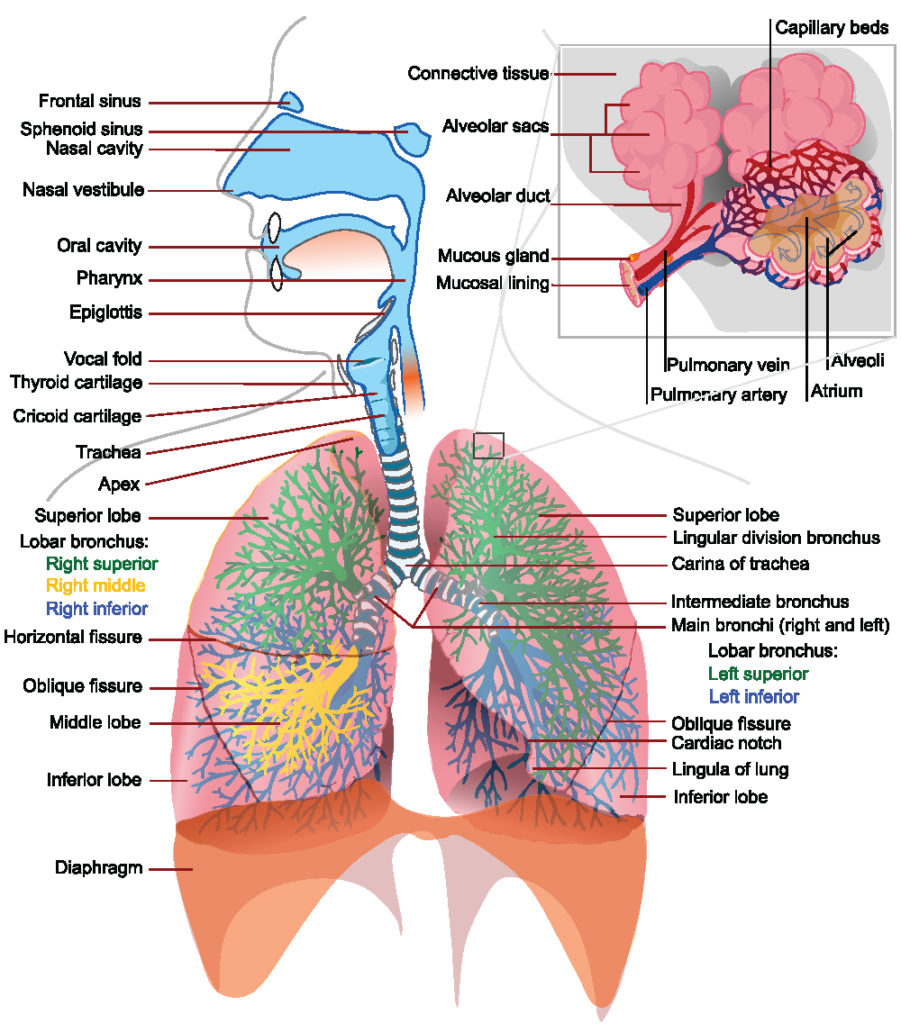
List the partial pressures for oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmospheric air alveoli arteriole blood tissue capillaries and venous blood. Exhalation is the flow of the breath out of an organism.
Mechanics Of Breathing Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
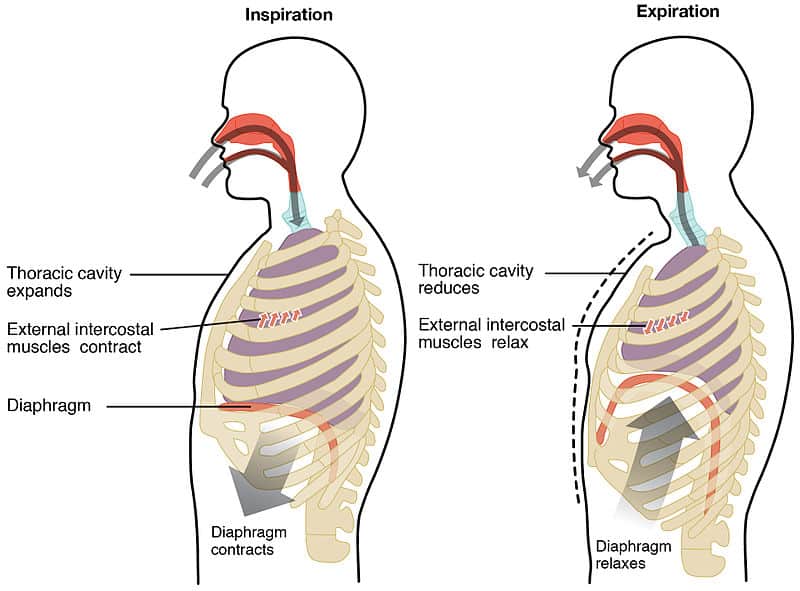
This action is also known as external respiration and is created by the muscles of the chest and the diaphragm changing the size of the chest cavity and air pressure.
. They relax during exhalation and turned into dome-shaped by moving up. Expiration is the phase of ventilation in which air is expelled from the lungs. If Antonio performed CPR steadily as described how much time has passed in three cycles of compressions and breaths.
This has the effect of decreasing the volume within the thoracic cavity and increasing the pressure within the lungs with respect to atmospheric pressure. Both of these actions cause the volume of the thorax chest cavity to increase which causes the pressure to decrease to below atmospheric. In response the elastic fibers in lung tissue cause the lungs to recoil to their original volume.
During expiration the relaxation of the diaphragm and elastic recoil of tissue decreases the thoracic volume and increases the intraalveolar pressure. Pulmonary ventilation consists of the process of inspiration or inhalation where air enters the lungs and expiration or exhalation where air leaves the lungs. The volume changes result in pressure changes which lead to the flow of gases to equalise the pressure.
Exhalation is the process of letting air out from lungs. The air then fills the space outside of the lung between the lung and chest wall. 1 point Describe the mechanical process of inspiration and expiration including the respiratory muscles that are involved the resulting changes in pressure increase or decrease and the.
Modes of mechanical ventilation are one of the most important aspects of the usage of mechanical ventilationThe mode refers to the method of inspiratory support. The entry and exit of air into and from the lungs are called inspiration and expiration respectively. A collapsed lung occurs when air escapes from the lung.
The process of exhalation occurs due to an elastic. Inhalation and exhalation are how your body brings in oxygen and gets rid of carbon dioxide. The role of intercostal muscle.
The process of exhaling carbon dioxide is called expiration. At the same time the muscles of the diaphragm contract pulling the diaphragm down and causing it to flatten. This happens due to elastic properties of the lungs as well as the internal intercostal muscles which lower the rib cage and decrease thoracic volume.
Inhalation is an active process. Expiration exhalation is the process of letting air out of the lungs during the breathing cycle. The pressure of the air inside the lungs then increases above the air pressure outside the body and air rushes out.
During normal expiration the external intercostals together with the diaphragm relax. The role of diaphragm. This movement of the muscles causes the lungs to expand and fill with air like a bellows inhalation.
Conversely when the muscles relax the thoracic cavity gets smaller the volume of the lungs decreases and air is expelled exhalation. Here we explain the mechanics of breathing and how breathing is regulated at rest. The process of inhalation occurs due to an increase in the lung volume diaphragm contraction and chest wall expansion which results in a decrease in lung pressure in comparison to the atmosphere.
Now the external intercostal muscles. Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. It then travels back to the heart as deoxygenated blood then returns to the lungs to be expelled as.
It is initiated by relaxation of the inspiratory muscles. He repeated these two stepsfour continuous cycles of compressions and breaths every minuteuntil the paramedics arrived to take over. In animals it is the movement of air from the lungs out of the airways to the external environment during breathing.
During exhalation the diaphragm is relaxed which decreases the volume of the lung cavity. Breathing or pulmonary ventilation has two phases - inspiration or inhalation and expiration or exhalation. The process of inhalation occurs due to an increase in the lung volume diaphragm contraction and chest wall expansion.
During inspiration the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles contract causing the rib cage to expand and move outward and expanding the thoracic cavity and lung volume. The process gets help from a large dome-shaped. Exhalation is a passive process.
Breathe in When a person inhales the diaphragm and the muscles between the ribs contract and expand the chest cavity. As the thoracic diaphragm relaxes during exhalation it causes. 3 points answer citation grammarspelling 2-Describe the mechanical process of exhalation.
Expiration occurs when the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles relax. 3 points answer citation grammarspelling 4-Explain external. Breathe out When a person exhales the diaphragm and muscles between the ribs relax and make the chest cavity smaller.
Key Points The mechanics of breathing follow Boyles Law which states that pressure and volume have an inverse relationship. While inspiration is active expiration is a passive process because it uses the elastic recoil of the muscles and lungs. Lab 12 Summary Objectives.
The action of breathing in and out is due to changes in pressure within the chest thorax. 1-Describe the mechanical process of inhalation. What Are the Steps Involved in Inhalation and Exhalation.
3 points answer citation grammarspelling 3-Explain internal respiration. Diaphragm relaxes to return to its resting position reducing the superiorinferior dimension of the thoracic cavity. Mechanics Mechanism Of Breathing.
A 45 seconds b 1 minute c 3 minutes d 3 minutes 45 seconds. It occurs when the size of the thoracic activity decreases and the air pressure outside increases. Describe the mechanism of inhalation.
Inhalation is now complete and the next step is exhalation. At the alveolicapillary red blood cells pick up the oxygen and take it to the heart from there it is taken to the muscles and various parts of the body. It is a passive process.
Chest injury ruptures blisters damaged lung tissue COPD cystic fibrosis pnemonia mechanical ventilation machine. Breathing is merely came mechanical process of inspiration and expiation whereas the process of respiration is a wider phenomenon that includes breathing transport and exchange of gases between lungs and tissues as well as the chemical. The external intercostal muscles contract pulling the ribs upwards and outwards.
They contract during the inhalation and get flattens by moving down. When the diaphragm contracts it moves down towards the abdomen. This buildup of air puts pressure on the lung so it cannot expand as much as it normally does when you take a breath.
It is a mechanical process that depends on volume changes in the chest cavity. The diaphragm relaxes and moves up and the relaxation of the intercostal muscles moves the ribs in and down. When you inhale you breath in oxygen which travels through the lungs to the alveolicapillary for gas exchange.

What Are The Mechanics Of Breathing
Mechanics Of Breathing Inspiration Expiration Teachmephysiology
0 Comments